Lungs: The Vital Organs for Breathing
The lungs are two spongy organs located in the chest, on either side of the heart. They play a critical role in the respiratory system, which is responsible for delivering oxygen to the body and removing carbon dioxide.

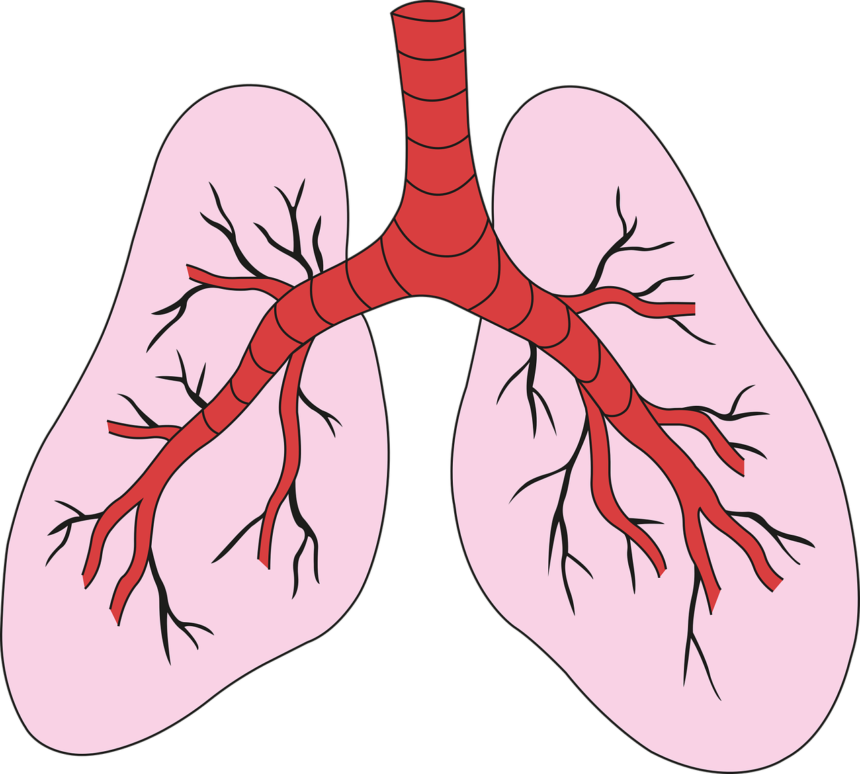
Structure of Lungs
The lungs are composed of several different structures, including bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. Bronchi are the large airways that branch off from the trachea, or windpipe, and lead into each lung. Bronchioles are smaller airways that branch off from the bronchi, and alveoli are the small air sacs located at the end of the bronchioles.
The alveoli are where the exchange of gases occurs. Oxygen from the air is taken up by the blood in the capillaries surrounding the alveoli, and carbon dioxide is released from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled.
Function of Lungs
The primary function of the lungs is to provide oxygen to the body and remove carbon dioxide. When we breathe in, air enters the nose or mouth and travels down the trachea, which divides into two bronchi, one leading to each lung. The bronchi then divide into smaller and smaller bronchioles, eventually leading to the alveoli.
In the alveoli, oxygen is transferred from the air to the blood, while carbon dioxide is transferred from the blood to the air. The oxygen-rich blood is then carried throughout the body by the circulatory system, while the carbon dioxide is exhaled.
Importance of Lungs
The lungs are vital organs that are essential for life. Without them, the body would not be able to get the oxygen it needs to function properly. The respiratory system and the lungs play a critical role in maintaining the acid-base balance in the body, which is necessary for many physiological processes.
The lungs also help to protect the body from infections and other harmful substances. The mucus lining in the airways traps bacteria, viruses, and other particles, preventing them from entering the body. The cilia, hair-like structures in the airways, move the mucus and trapped particles out of the lungs and into the throat, where they can be coughed up or swallowed.
The lungs also play a crucial role in regulating blood pressure. When we breathe, the lungs produce a gas called nitric oxide, which helps to dilate the blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing blood pressure.
Maintaining Lung Health
Maintaining lung health is crucial for overall health and well-being. Here are some tips to keep your lungs healthy:
Quit smoking:
Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer and other lung diseases. Quitting smoking is the best thing you can do for your lung health.
Avoid exposure to pollutants:
Exposure to pollutants such as air pollution, chemicals, and fumes can damage the lungs. Take steps to reduce your exposure to these substances.
Exercise regularly:
Regular exercise can help improve lung function and capacity, as well as overall health.
Practice good hygiene:
Wash your hands regularly and avoid close contact with people who are sick to reduce the risk of respiratory infections.
Get regular check-ups:
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help identify any lung problems early, when they are most treatable.
Final Thoughts
The lungs are vital organs that play a critical role in the respiratory system and maintaining overall health. Understanding how they work and how to keep them healthy is essential for a healthy life. By taking steps to maintain lung health, you can help ensure that your body gets the oxygen it needs to function properly.