Ozempic® (Semaglutide): A Comprehensive Guide to the Diabetes and Weight Management Medication
Introduction: Understanding the Ozempic Phenomenon
In recent years, Ozempic® has emerged as one of the most discussed medications in healthcare, transforming treatment approaches for type 2 diabetes and chronic weight management. As a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, Ozempic offers patients a unique combination of benefits that extend far beyond simple blood sugar control. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about this groundbreaking medication—from its mechanism of action and proper administration to potential side effects and real-world patient experiences.
Developed by Novo Nordisk and first approved by the FDA in 2017, Ozempic contains the active ingredient semaglutide and is administered via a once-weekly subcutaneous injection. While originally developed for type 2 diabetes management, its effects on appetite regulation and weight loss have generated significant attention, leading to both appropriate medical use and important conversations about its proper application.

How Ozempic Works: The Science Behind Semaglutide
Mechanism of Action
Ozempic works by mimicking the action of GLP-1, a natural hormone in your body that plays multiple roles in metabolism. When you take Ozempic, it activates GLP-1 receptors throughout your body, resulting in several beneficial effects:
- Stimulates insulin secretion: In response to elevated blood sugar, semaglutide prompts the pancreas to release more insulin, helping move glucose from the bloodstream into cells.
- Suppresses glucagon secretion: Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood sugar. Ozempic inhibits its release, contributing to better blood sugar control.
- Slows gastric emptying: By slowing down how quickly food leaves the stomach, Ozempic helps regulate glucose absorption and contributes to feelings of fullness.
- Reduces appetite: Through direct effects on the brain’s appetite centers, Ozempic helps decrease food cravings and intake.
At the molecular level, semaglutide binds to GLP-1 receptors, increasing intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels and activating protein kinase A (PKA), which is involved in insulin synthesis and secretion.
Pharmacological Profile
Semaglutide is 94% similar to human GLP-1 and has been chemically modified to resist degradation by enzymes, giving it an extended half-life of approximately 165 hours (about one week). This allows for once-weekly dosing rather than the multiple daily injections required by earlier diabetes medications.
The medication achieves 89% bioavailability when administered subcutaneously, with peak concentrations reached within 1-3 days and steady-state achieved after 4-5 weeks of regular dosing.

FDA-Approved Uses and Indications
Ozempic has received FDA approval for several specific medical uses:
- Improving glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus, alongside diet and exercise.
- Reducing the risk of major cardiovascular events (cardiovascular death, non-fatal heart attack, or non-fatal stroke) in adults with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease.
- Reducing the risk of sustained eGFR decline, end-stage kidney disease, and cardiovascular death in adults with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease.
It’s important to note that while Ozempic often results in weight loss and is sometimes prescribed “off-label” for weight management, it is not FDA-approved specifically as a weight loss drug. For chronic weight management, Wegovy (which contains a higher dose of the same active ingredient, semaglutide) holds the specific FDA approval.
Proper Dosing and Administration
Standard Dosing Schedule
Ozempic follows a gradual dose escalation protocol to help your body adjust to the medication and minimise side effects:
| Treatment Week | Dose | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Weeks 1-4 | 0.25 mg once weekly | Starting dose to help your body adjust |
| Week 5 onward | 0.5 mg once weekly | Initial therapeutic dose |
| After at least 4 weeks at 0.5 mg | 1 mg once weekly | For additional blood sugar control if needed |
| Maximum dose | 2 mg once weekly | For patients requiring additional A1C control |
Table: Ozempic standard dosing schedule
Administration Guidelines
- Frequency: Take once weekly on the same day each week.
- Timing: Can be taken at any time of day, with or without food.
- Injection sites: Subcutaneous injection in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. Rotate injection sites weekly to prevent skin irritation.
- Missed dose: If you miss a dose, take it as soon as possible within 5 days after the missed dose. If more than 5 days have passed, skip the missed dose and take your next dose on the regular schedule.
- Day change: You may change your injection day if needed, as long as the last dose was taken at least 2 days (48 hours) before.
Preparation and Injection Technique
Proper injection technique is crucial for safety and effectiveness:
- Prepare: Check that the liquid in the pen is clear and not cloudy. Always use a new needle for each injection.
- Check flow (for new pens only): Before your first injection with a new pen, perform a flow check to ensure the pen is working properly.
- Select dose: Turn the dose selector until your prescribed dose appears in the dose counter.
- Inject: Insert the needle into your skin, press and hold the dose button until the dose counter shows “0.” Keep the needle in place and count slowly to 6 to ensure the full dose is delivered.
- Dispose safely: Dispose of used needles in an FDA-approved sharps container or a sturdy plastic household container.
Never share your Ozempic pen with another person, even if you change the needle, as this can spread serious infections.
Potential Side Effects and Safety Considerations
Common Side Effects
Most side effects are gastrointestinal and tend to improve over time as your body adjusts to the medication:
- Nausea (most common)
- Vomiting
- Diarrhoea
- Constipation
- Abdominal pain
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Indigestion or heartburn
These symptoms are most likely to occur when first starting Ozempic or after a dose increase and typically subside within several weeks.
Serious Side Effects and Warnings
While less common, Ozempic carries several important safety warnings:
- Risk of thyroid C-cell tumors: In rodent studies, semaglutide caused thyroid C-cell tumors. While human relevance is unknown, Ozempic is contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2).
- Pancreatitis: Acute pancreatitis has been reported in patients taking GLP-1 receptor agonists. Watch for severe abdominal pain that may radiate to the back, with or without vomiting.
- Diabetic retinopathy complications: In clinical trials, more events of diabetic retinopathy complications occurred with Ozempic (3.0%) versus placebo (1.8%), particularly with rapid improvement in glucose control.
- Acute kidney injury: Dehydration from gastrointestinal side effects like vomiting and diarrhea may lead to kidney injury, especially in those with pre-existing kidney problems.
- Gallbladder problems: Including gallstones and gallbladder disease.
- Intestinal obstruction: Post-market reports of ileus (intestinal blockage) led to an FDA label update.
Managing Side Effects
To help manage common side effects:
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals to reduce nausea
- Avoid high-fat, greasy, or spicy foods
- Stay well-hydrated, especially if experiencing vomiting or diarrhea
- Include fiber-rich foods to minimise constipation
- Discuss persistent side effects with your healthcare provider—they may adjust your dosing schedule
Ozempic vs. Wegovy: Understanding the Difference
Many patients confuse Ozempic with Wegovy since both contain semaglutide. Here’s a clear comparison:
| Aspect | Ozempic | Wegovy |
|---|---|---|
| FDA Approval | Type 2 diabetes management | Chronic weight management |
| Standard Doses | 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 2 mg | 0.25 mg, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, 1.7 mg, 2.4 mg |
| Maximum Dose | 2 mg once weekly | 2.4 mg once weekly |
| Primary Purpose | Blood sugar control + cardiovascular risk reduction | Weight loss |
| Typical Weight Loss | ~8-14 lbs (as observed in diabetes trials) | ~15% of body weight (in weight management trials) |
Table: Comparison of Ozempic and Wegovy
While the medications contain the same active ingredient, they are approved for different purposes and typically prescribed at different dose ranges. Wegovy is specifically approved for chronic weight management in adults with obesity (BMI ≥30) or overweight (BMI ≥27) with at least one weight-related condition.
Real Patient Experiences and Outcomes
Patient stories provide valuable insight into the real-world impact of Ozempic:
Michael’s Story: An award-winning musician who lowered his A1C under 7% and lost weight while managing his type 2 diabetes, allowing him to continue performing and inspiring others through music.
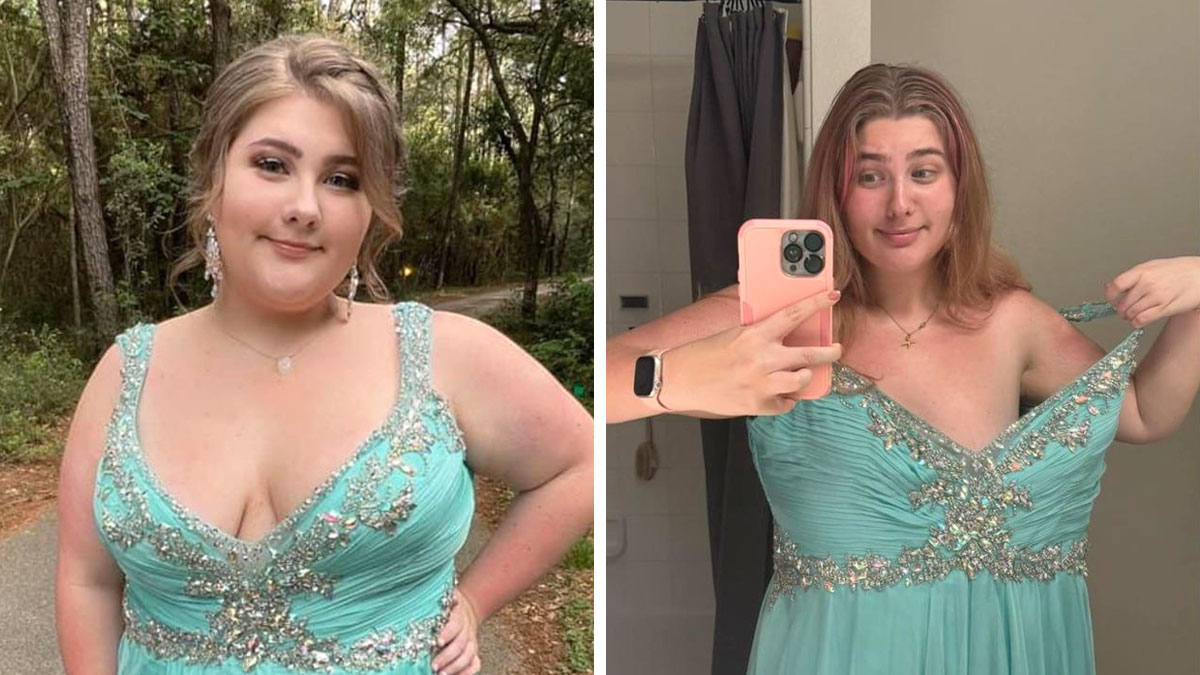
Hailey’s Journey: After weight gain during lockdowns, Hailey began semaglutide treatment and lost 26 kilograms (about 57 pounds) over nine months. She reported that the medication helped “rewire” her relationship with food, noting: “I’ve always used food as a coping mechanism… Now, if I’m stressed out but not hungry, I’ll go to the gym, for a walk, or find something to do that’s not food-related”.
Maria’s Experience: A salon owner and mother who lowered her A1C under 7% while managing a busy schedule. She emphasized the importance of finding the right treatment plan that fits her lifestyle.
These stories highlight that success with Ozempic typically involves combining medication with lifestyle changes like diet modifications and increased physical activity.
Drug Interactions and Special Considerations
Common Interactions
- Other diabetes medications: Ozempic may increase the risk of hypoglycemia when combined with insulin or insulin secretagogues (like sulfonylureas). Your doctor may need to adjust your other diabetes medications.
- Oral medications: Since Ozempic slows gastric emptying, it might affect the absorption of other oral medications. Take special care with medications that require specific timing or blood levels.
- Statins: Many patients wonder if they can take Ozempic with cholesterol medications like statins. Generally, these can be safely combined, and may offer complementary benefits for cardiovascular health.
Special Populations
- Chronic kidney disease: For patients with chronic kidney disease, after at least 4 weeks at the 0.5 mg dose, your healthcare provider may recommend increasing to 1 mg.
- Elderly patients: No dosage adjustment is specifically recommended, but careful monitoring is advised.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Ozempic is not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Discuss alternative treatments with your healthcare provider if you’re planning pregnancy or become pregnant while taking Ozempic.
Cost and Insurance Coverage
The cost of Ozempic varies significantly based on insurance coverage:
- Without insurance: Approximately $800-$1,000 per month in the United States.
- With commercial insurance: 98% of commercial patients have coverage for Ozempic, though prior authorization may be required.
- Savings programs: Novo Nordisk offers a savings card that may reduce copays for eligible commercially insured patients.
Many patients find that the potential long-term savings from avoiding diabetes complications outweigh the medication costs, though this is an individual consideration that should be discussed with your healthcare provider.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to see results with Ozempic?
- Blood sugar effects: Many patients notice improvements in blood sugar within the first few weeks.
- Weight loss: Clinical trials showed weight loss beginning within the first month, with increasing effects over time.
- Full therapeutic effect: Maximum benefits for blood sugar control are typically seen after 8-12 weeks of consistent use at your maintenance dose.
Can I stop Ozempic once I reach my goals?
Ozempic is generally considered a long-term medication for chronic conditions. If you stop taking it:
- Blood sugar levels will likely rise if you have diabetes
- Weight loss may plateau or reverse
- Any cardiovascular benefits would diminish
Always consult your healthcare provider before making changes to your medication regimen.
What happens if I miss a dose?
If you miss a dose of Ozempic, take it as soon as possible within 5 days after the missed dose. If more than 5 days have passed, skip the missed dose and take your next dose on the regular schedule. Do not take two doses within 48 hours of each other.
Are “Ozempic face” and “Ozempic butt” real side effects?
These terms refer to cosmetic changes from rapid weight loss, not direct medication side effects. When people lose weight quickly, they may experience sagging skin or changes in fat distribution. These effects are related to the weight loss itself rather than a specific action of the medication.
Can I drink alcohol while taking Ozempic?
Moderate alcohol consumption is generally acceptable, but be aware that:
- Ozempic may increase alcohol sensitivity
- Alcohol can affect blood sugar levels
- Combining alcohol with Ozempic might increase gastrointestinal side effects
Always drink responsibly and monitor your body’s response.
How should I store Ozempic?
- Unopened pens: Store in the refrigerator at 36-46°F (2-8°C). Do not freeze.
- In-use pen: Can be stored at room temperature (59-86°F or 15-30°C) for up to 8 weeks.
- Always protect from extreme heat and direct light.
Conclusion: Is Ozempic Right for You?
Ozempic represents a significant advancement in the management of type 2 diabetes and related metabolic conditions. Its once-weekly dosing, proven cardiovascular benefits, and positive effects on weight make it an attractive option for many patients. However, it’s not suitable for everyone, and potential side effects must be carefully considered.
The most successful Ozempic patients typically:
- Work closely with their healthcare team to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed
- Combine medication with sustainable lifestyle changes
- Report side effects promptly to manage them effectively
- Have realistic expectations about results and timelines
If you’re considering Ozempic, the next step is a thorough discussion with your healthcare provider about whether it aligns with your specific health profile, goals, and lifestyle. With proper medical supervision and patient commitment, Ozempic can be a powerful tool in managing type 2 diabetes and improving overall metabolic health.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before starting or changing any medication or treatment plan. Individual results may vary.