The Prostate Gland: Understanding its Importance and Common Health Concerns
Introduction
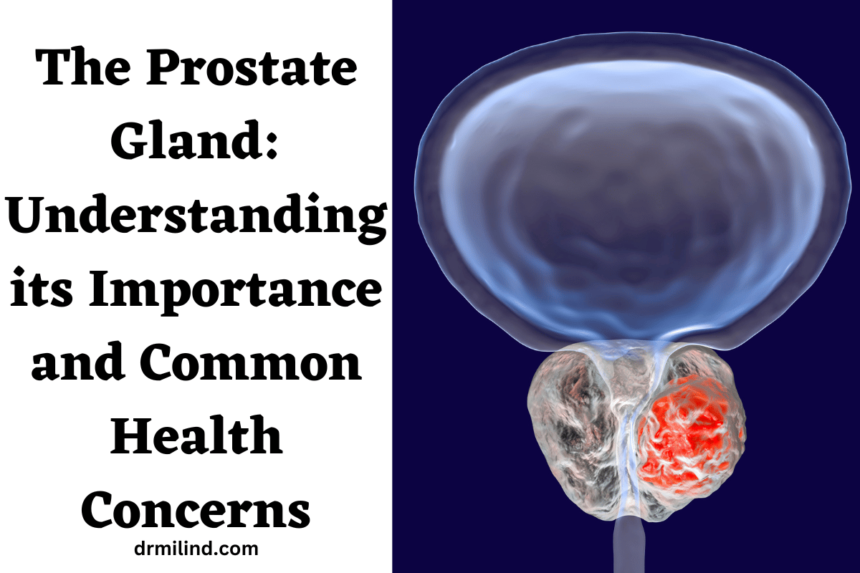
The prostate gland, a walnut-sized organ located just below the bladder, plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system. While often overlooked or misunderstood, this small gland is responsible for producing a significant portion of the fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of the prostate gland, its functions, potential health issues, and the importance of regular prostate health check-ups.
Anatomy and Functions of the Prostate Gland
The prostate gland is a vital part of the male reproductive system, surrounding the urethra, the tube responsible for carrying urine and semen out of the body. It consists of glandular tissue and muscle fibers, which work together to produce and release seminal fluid during ejaculation.
The primary functions of the prostate gland include:
Seminal Fluid Production:
The prostate gland secretes a milky, alkaline fluid that combines with sperm from the testes and fluids from other glands to form semen. This fluid provides nutrients, protection, and increased motility to the sperm.
Ejaculation Control:
The prostate gland also aids in controlling the release of urine and semen by contracting and closing off the opening between the bladder and urethra during sexual activity.
Common Prostate Health Concerns
Despite its significance, the prostate gland is prone to several health issues. The most common conditions affecting the prostate are:
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH):
BPH is characterised by the enlargement of the prostate gland, causing urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, weak urine flow, and difficulty starting and stopping urination. While BPH is not cancerous, it can significantly impact a man’s quality of life.
Prostatitis:
Prostatitis refers to the inflammation of the prostate gland, which can be caused by bacterial infection or other factors. Symptoms may include pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, urinary difficulties, and sexual dysfunction.
Prostate Cancer:
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers among men. It occurs when cells in the prostate gland grow uncontrollably. Early-stage prostate cancer often shows no symptoms, which makes regular screenings vital for early detection. If diagnosed early, treatment options, including surgery, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy, can be effective.
Maintaining Prostate Health
Taking proactive steps to maintain a healthy prostate is crucial for men of all ages. Here are some essential tips to promote prostate health:
- Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can contribute to overall prostate health. Certain foods, such as tomatoes, broccoli, and green tea, have shown potential benefits in reducing the risk of prostate problems.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity regularly not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also reduces the risk of developing prostate issues. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise each week, along with strength-training exercises.
- Annual Check-ups: Men over the age of 50, or those with a family history of prostate issues, should consider regular prostate health check-ups. These may include a digital rectal exam (DRE) and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test.
Treatment Options for Prostate Health
When it comes to addressing prostate health concerns, several treatment options are available depending on the specific condition. Here are some common treatment approaches for various prostate issues:
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH):
- Medications: Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors are commonly prescribed to manage BPH symptoms by relaxing the muscles of the prostate and reducing its size.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Procedures like transurethral microwave therapy (TUMT), transurethral needle ablation (TUNA), and laser therapy can be effective in reducing prostate enlargement and improving urinary symptoms.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases, surgical procedures such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or laser enucleation may be recommended to remove or reduce the size of the prostate gland.
Prostatitis:
- Antibiotics: Bacterial prostatitis is treated with a course of antibiotics specific to the type of bacteria causing the infection.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Non-bacterial prostatitis is often managed with pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications to alleviate symptoms.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Practicing relaxation techniques, avoiding irritants, and adopting a healthy diet can help manage symptoms of prostatitis.
Prostate Cancer:
- Active Surveillance: For low-risk, slow-growing prostate cancer, active surveillance involves regular monitoring with PSA tests, digital rectal exams, and occasional biopsies to determine if treatment is necessary.
- Surgery: Radical prostatectomy involves the removal of the prostate gland and surrounding tissues. It is a common treatment option for localized prostate cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy radiation is used to target and destroy cancer cells in the prostate gland. It can be administered externally (external beam radiation) or internally (brachytherapy).
- Hormone Therapy: Prostate cancer cells rely on male hormones for growth. Hormone therapy aims to suppress the production or block the action of these hormones to slow down cancer progression.
- Chemotherapy: In advanced cases of prostate cancer, chemotherapy drugs may be used to target cancer cells that have spread beyond the prostate.
It is crucial for individuals to consult with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their specific condition, stage of disease, overall health, and personal preferences. Each treatment option carries its benefits, risks, and potential side effects, which should be thoroughly discussed and considered.
Home Remedies for Prostate Health
While home remedies may not treat or cure prostate conditions on their own, they can complement medical treatments and contribute to overall prostate health. Here are some home remedies that may help promote prostate health:
Healthy Diet:
- Include fruits and vegetables: Consume a variety of fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants and vitamins. Examples include tomatoes, broccoli, berries, spinach, and carrots.
- Healthy fats: Incorporate foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel) and flaxseeds, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Reduce red meat and processed foods: Limit the consumption of red meat and processed foods, as they may contribute to inflammation and increased risk of prostate issues.
Regular Exercise:
- Engage in aerobic exercises: Regular aerobic activities like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling can help maintain a healthy weight and promote overall well-being.
- Kegel exercises: These exercises involve contracting and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles, which can help strengthen the muscles supporting the prostate.
Herbal Supplements:
- Saw palmetto: Saw palmetto extract is a popular herbal supplement used for prostate health, particularly for managing BPH symptoms.
- Pygeum: Pygeum extract, derived from the bark of the African plum tree, is believed to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help alleviate urinary symptoms related to BPH.
- Beta-sitosterol: This plant sterol is found in various fruits, vegetables, and nuts. It is available in supplement form and may help improve urinary symptoms associated with BPH.
Stress Management:
- Practice relaxation techniques: Engage in activities that promote relaxation and reduce stress, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or tai chi.
- Get sufficient sleep: Prioritise quality sleep to support overall well-being and stress reduction.
Hydration:
- Drink an adequate amount of water: Staying hydrated helps maintain urinary tract health and can support overall prostate function.
It is essential to note that while these home remedies may have potential benefits, they should not replace medical advice or treatment prescribed by healthcare professionals. If experiencing symptoms or concerns regarding prostate health, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Conclusion
The prostate gland, often overshadowed by more prominent organs, plays a vital role in male reproductive health. Understanding its functions, common health concerns, and implementing preventive measures can contribute to a healthier and more fulfilling life. Regular check-ups and adopting a balanced lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of prostate-related issues, ensuring men can lead a life of vitality and well-being.