IBD
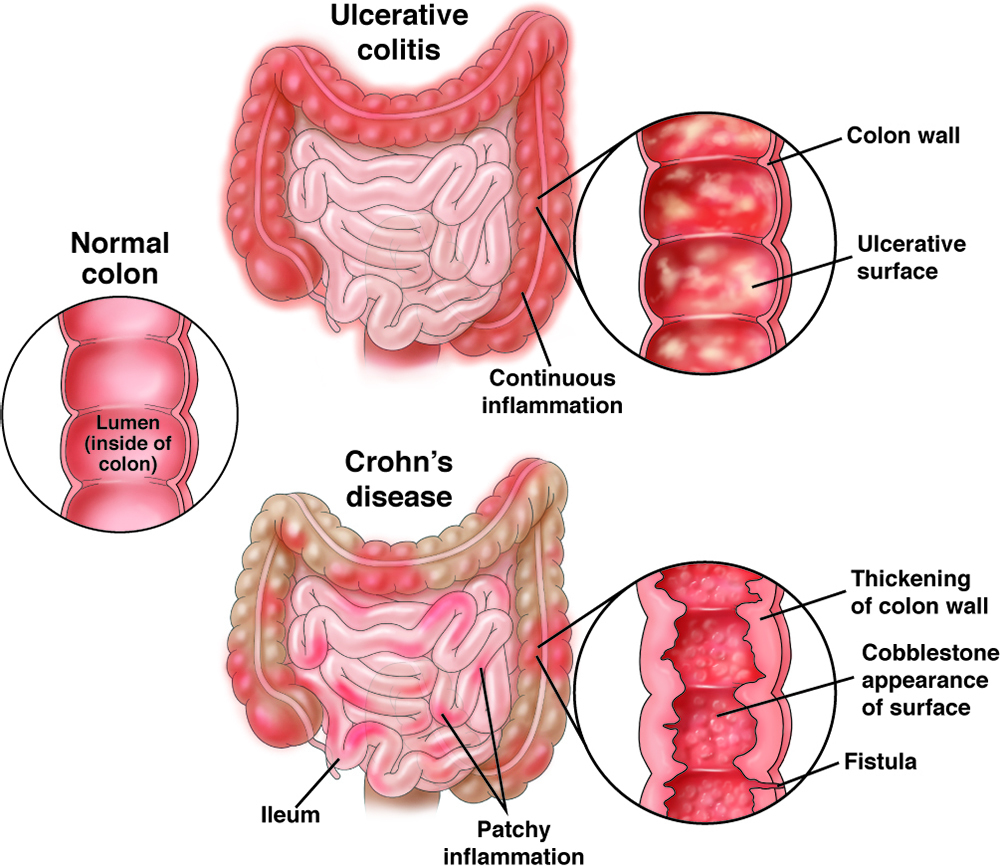
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory condition of the gastrointestinal tract. It is a term used to describe two primary types of chronic inflammatory bowel diseases, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Although the symptoms and causes of the two conditions are different, they share common characteristics such as chronic inflammation and damage to the digestive tract.
What is IBD?
IBD is a chronic condition that causes inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. It is a group of conditions that includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. IBD affects people of all ages, but it usually starts in adolescence or early adulthood.
Causes of IBD
The exact cause of IBD is unknown, but research suggests that genetics, environmental factors, and an abnormal immune response play a role. People with a family history of IBD are more likely to develop the condition. Smoking, a high-fat diet, and a sedentary lifestyle can increase the risk of IBD.
Symptoms of IBD
The symptoms of IBD can vary from person to person and can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms of IBD include abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, fatigue, weight loss, and fever. In severe cases, IBD can cause complications such as bowel obstruction, abscesses, and perforation of the bowel.
Diagnosis of IBD
IBD is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. A colonoscopy, which is a procedure that uses a long, flexible tube with a camera on the end to examine the inside of the colon, is often used to diagnose IBD. Biopsies of the intestinal tissue can also be taken during the procedure to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of IBD
The treatment of IBD aims to reduce inflammation, control symptoms, and prevent complications. Medications such as corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and biologic agents are commonly used to treat IBD. Lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet can also help manage the symptoms of IBD.
Living with IBD
Living with IBD can be challenging, but it is possible to lead a full and active life with the condition. It is important to work closely with a healthcare team to manage the symptoms of IBD and prevent complications. Support groups can also provide valuable emotional support and practical advice for people with IBD and their families.
Conclusion
Inflammatory bowel disease is a chronic inflammatory condition of the gastrointestinal tract that affects millions of people worldwide. Although the exact cause of IBD is unknown, research suggests that genetics, environmental factors, and an abnormal immune response play a role. The symptoms of IBD can vary from person to person and can range from mild to severe. The treatment of IBD aims to reduce inflammation, control symptoms, and prevent complications. It is important to work closely with a healthcare team to manage the symptoms of IBD and prevent complications.











