Understanding Osteoarthritis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. This condition causes the cartilage in joints to wear down, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. While osteoarthritis is most commonly associated with older adults, it can affect people of all ages. In this blog post, we will explore what osteoarthritis is, what causes it, and how it can be treated, Breaking the Joint Pain Cycle: Understanding and Managing Osteoarthritis.
What is Osteoarthritis?
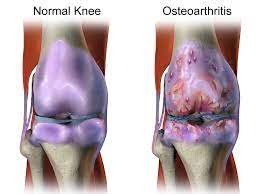
Osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that affects the joints, particularly the ones in the hands, knees, hips, and spine. It is a progressive condition that slowly wears away the cartilage that cushions the joints, causing bones to rub against each other. This results in pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
What Causes Osteoarthritis?
The exact cause of osteoarthritis is not known. However, certain factors are known to increase the risk of developing this condition. These factors include:
- Age: Osteoarthritis is more common in people over the age of 50.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis than men.
- Genetics: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to developing osteoarthritis.
- Joint injury: Previous injuries to the joint can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis.
- Obesity: Being overweight puts extra pressure on the joints, which can increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Joint deformities: People with joint deformities are more likely to develop osteoarthritis.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
The symptoms of osteoarthritis can vary from person to person, but they generally include:
- Pain: The most common symptom of osteoarthritis is pain in the affected joint. The pain is usually worse after activity and improves with rest.
- Stiffness: Osteoarthritis can cause stiffness in the affected joint, particularly in the morning or after sitting for a long time.
- Swelling: The affected joint may become swollen and tender.
- Reduced mobility: Osteoarthritis can make it difficult to move the affected joint, which can limit mobility.
- Grating sensation: Some people may experience a grating sensation when moving the affected joint.
Treatment Options for Osteoarthritis
There is no cure for osteoarthritis, but there are several treatment options that can help manage the symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. These treatment options include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve joint mobility and strength, as well as reduce pain and stiffness.
- Weight loss: Losing weight can help reduce the pressure on the affected joint and slow down the progression of osteoarthritis.
- Assistive devices: Assistive devices, such as braces and shoe inserts, can help support the affected joint and reduce pain.
- Surgery: In severe cases of osteoarthritis, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the affected joint.
Preventing Osteoarthritis
While it is not possible to prevent osteoarthritis entirely, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing this condition. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight puts extra pressure on the joints, which can increase the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Exercising regularly: Regular exercise can help keep the joints healthy and reduce the risk of osteoarthritis.
- Avoiding joint injuries: To reduce the risk of developing osteoarthritis, it is important to avoid joint injuries as much as possible. This can be done by using proper protective equipment when engaging in sports or other physical activities.
- Taking breaks during repetitive activities: Repetitive motions, such as typing or playing an instrument, can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis. It is important to take breaks and stretch during these activities to reduce the strain on the joints.
- Eating a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation and promote overall joint health.
- Managing other health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as diabetes and high blood pressure, can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis. It is important to manage these conditions through lifestyle changes and medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis is a common condition that affects the joints and can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, there are several treatment options available to manage the symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. It is also possible to reduce the risk of developing osteoarthritis through lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and exercising regularly. By taking steps to prevent and manage osteoarthritis, it is possible to maintain joint health and improve overall quality of life.